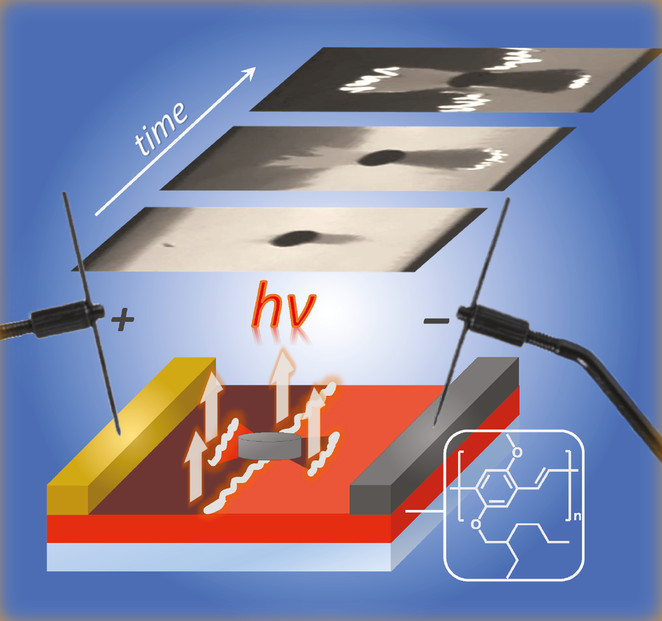
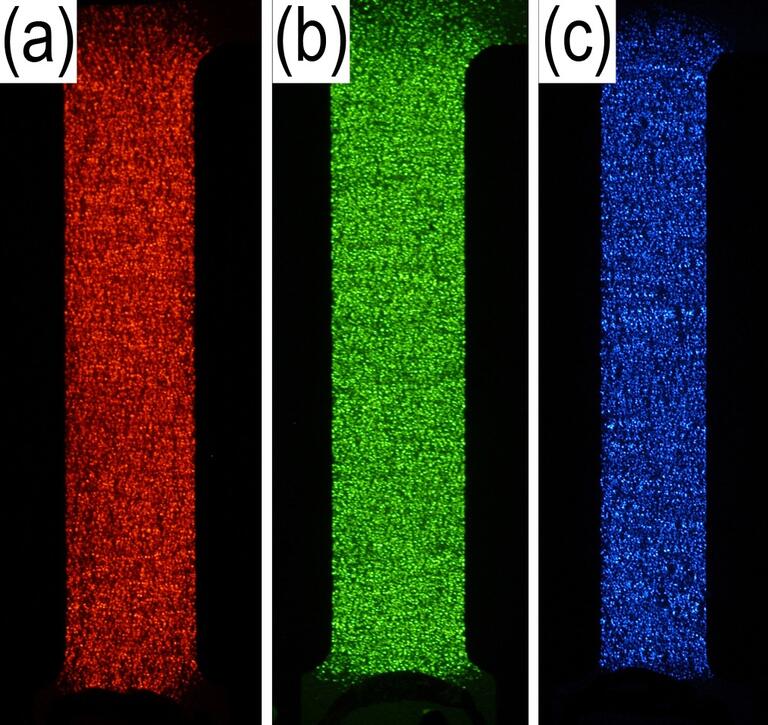
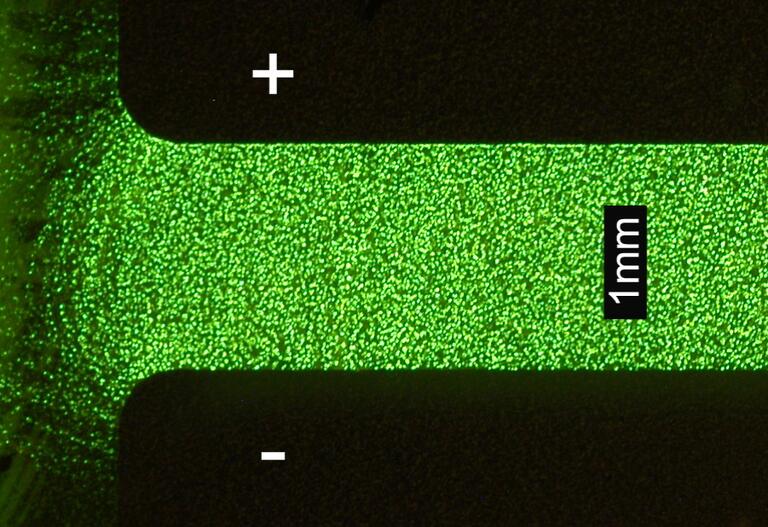
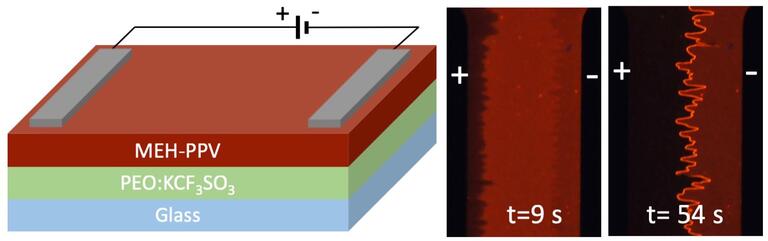
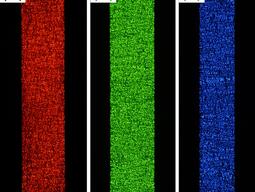
Our research on organic photonics and iontronics straddles the boundaries of condensed matter physics, device physics, photo-physics, and solid polymer electrolytes. We use direct imaging and optical probing to explore the emerging sciences of mixed organic semiconductors in which electrons, ions and photons interact in many unexpected ways. Our multi-disciplinary research has potential applications in renewable energy, solid state lighting and energy storage.










Recent Publications
-
Goyal, A., Wang, D. and Gao, J. (2023) Extremely large polymer light-emitting electrochemical cells with concentric circular electrodes Advanced Materials Technologies 2300824 Editor's Choice
-
Wang, D. and Gao, J. (2023) Electrical treeing and luminescence in a polymer p-n junction under extreme reverse bias Optical Materials 137:113524
-
Tong, C., Goyal, A., Wang, D. and Gao, J. (2022) Visualizing the effects of salt concentration in planar polymer light-emitting electrochemical cells. Electrochimica Acta 423:140574
-
Hu, S., Yeh, HW, and Gao, J. (2021) Polymer light-emitting electrochemical cells with ultraslow salt content: performance enhancement through synergetic chemical and electrochemical doping actions. Materials Chemistry Frontiers. 5: 1847
-
Wang, D., Hu, S., and Gao, J. (2021) Temperature Hypersensitive Organic Electroluminescence in a Reverse Biased, Frozen Polymer P–I–N Junction. Advanced Optical Materials. 2101033
-
Birdee, K., Hu, S., and Gao, J. (2020) Strong Doping and Electroluminescence Realized by Fast IonTransport through a Planar Polymer/Polymer Interface in Bilayer Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. 12: 46381-46389
-
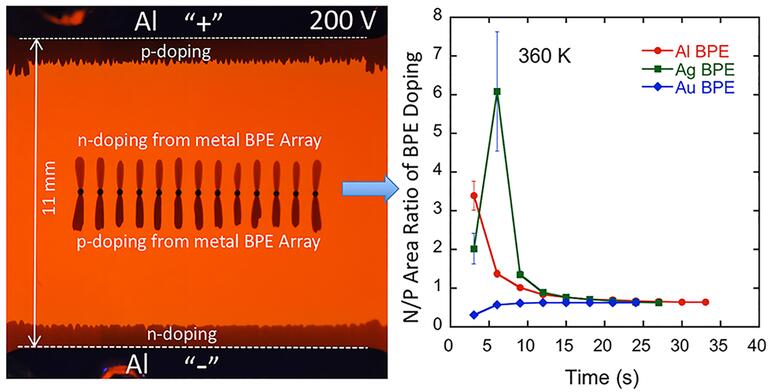
Hu, S. and Gao, J. (2020). Shaping Electroluminescence with a Large, Printed Bipolar Electrode Array: Solid Polymer Electrochemical Cells with Over a Thousand Light-Emitting p–n Junctions. ChemElectroChem. 7: 1748-1751.
-
Hu, S. and Gao, J. (2020). Polymer Light-Emitting Electrochemical Cells with Bipolar Electrode-Dynamic Doping and Wireless Electroluminescence. Advanced Functional Materials. 30 (33): 1907003. Invited review article.
Our research is funded by: