Organic Compound Analysis
Most of the organic analyses that we conduct are for organic priority pollutants such as pesticides, PCBs, PHCs, BTEX, VOC's PAH's and other petroleum products. Gas Chromatography (GC) is the standard methodology. From sample matrices such as soil, water, plants and fish, the analyte's are extracted into organic solvents, separated from interfering substances (cleaned up), concentrated and run on the GCs.

Using a variety of different detectors, excellent sensitivity and specificity can be achieved for a whole spectrum of compounds. The use of automated sample carousels means that the GCs can be left unattended for overnight operation.
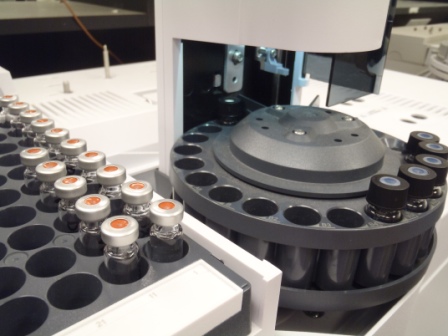
Automated sample analysis on Agilent GC
Sample Preparation For GC Analysis
There are many 'method specific' procedures we use to prepare our organic samples for GC analysis. Two of our primary solvent extraction methods utilize accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) or soxhlet extraction techniques.

Dionex ASE200 Solvent Extractor
Soxhlet Extraction
This glass apparatus was invented in 1879 and is still in use today. It uses the principle of 'continuous extraction' to repeatedly cycle solvent through a 'thimble' containing a material to be extracted.
See Wikipedia: Soxhlet Apparatus

Plant sample extraction by soxhlet
Detectors
The Electron Capture Detector (ECD)
From Agilent eInspirations newsletter 2010
The Flame Ionisation Detector (FID)
The Thermal Conductivity Detector (TCD)
See LibreTexts: Chemistry for complete descriptions of these detectors.
Typical PCB Chromatogram
Reproduced from "β-cyclodextrin enhanced phytoremediation of aged PCBs-contaminated soil from e-waste recycling area"
Yingxu Chen* a, Xianjin Tanga, Sardar Alam Cheemaa, Wenli Liub and Chaofeng Shena